>> Top >> Research plan >> Vision and image information processing group
![]()
I. Research on Visual Information Processing
"Toward elucidation of human vision and its application to engineering "
1. Elucidation of the mechanism of visual information processing
in thehuman brain
by measurements and analysis of the visual evoked potential and the visual
event-related potential
When one does some works, it takes the following process: vision or sensation > cognition > evaluation > decision > behavior. Generally,
the sensory evoked potential (SEP) has been availed to understand the vision
or the sensation in the above process. But recently, the event-related potential
(ERP) has introduced to investigate the higher order information processing
after the cognition in the above process. For instance, a component P300, a
positive potential change after the 300 msec when a stimulus is presented,
the brain wave contained in the ERP varies with discrimination of the stimulus.
This is affected by a strategy to the response and the attention. It is said
that the component P300 reflects the cognition process of a human. A change
of P300 is supposed to be a result from a change of information process related
to above these effects. By these change of ERP, we can treat the information
process in the brain. The present research attempts to elucidate a mechanism
of visual information processing in the human brain by measuring ERP, analyzing
the data on bipolar equi-potential inference method. Further, this enables
to superimpose the results on MRI, therefore we can identify the position in
3-dimensional brain.

Digital Electroencepharograph
2.Eye movements measurement in 3-D virtual space by use of liquid
crystal glasses.
By a 3-D display system with a liquid crystal glasses SB300 (Solidray, Co. Ltd),
we made a virtual 3-D display system. The system enables to display virtual 3-D
images from CCD cameras, etc. The system is combined with an Eye Mark Recorder
EMR-8 (NAC. Co. Ltd), and can measure eye movements on liquid crystal glasses.
We can compare eye movements between in a real vision and in a virtual vision.

Eye Mark Recorder System
3. Application of the peripheral vision to self-control robot Khepera.
Effective motion could be realized by applying the peripheral vision that
is one of the remarkable functions of human vision. This function was applied
for sensor system of a self-controlled micro robot Khepera Applied AI. We
compared the sensor systems with peripheral vision and without peripheral
vision under experiments for passing through a labyrinth. By a statistical
test for the durations of passing time through that, the effectiveness of
peripheral vision was assumed. Human activities always involves fuzziness,
further effective motion will be obtained to apply fuzzy control.
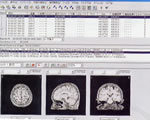
Bipolar Inference of Vision Evoked Potentials (NEC Medical)
III. Research on Optical and Image Information
Processing
"Integrated Electronics of Light and Image"
Optical waves have features of (1) the high propagation velocity (2) high
optical frequencies and short wavelengths, (3) capability of processing spatial
information, and (3) availability of various information carriers of intensity,
phase, polarization, wavelength, coherence and so on. On the basis of these
advantages, optical technologies are utilized in a wide range of fields concerning
high-speed and large scale transmission of information, local concentration
of energy, parallel data processing, and high precision measurement. On the
other hand, image processing based on the digital technology has features of
(1) applicability of various mathematical processing due to high flexibility
of data operations, (2) high robustness to noise, and (3) eligibility for intelligent
processing on the basis of the computer technology. Optical and image processing
technologies are expected to play a key role as one of leading technologies
achieving further high-tech information society in the future
This research is concerned with light and image that are basis for various
optical technologies, and aims to study both optical phenomena as information
carriers on objects and processing of images as detected optical data,
in an integrated way, and to associate them to various applications. In
other words, by integrating different theories in optics for various optical
devices and image detectors, and image processings, we aim to establish
novel optical technologies as an integrated and optimized combination of
optical and information technologies. These are achieved by studying the
light that transmits and processes information in the form of wave propagation,
optical systems that image the propagating waves, photodetectors and image
sensors, and digital image processing techniques that facilitate sophisticated
mathematical and intelligent processings and human recognition of the detected
images. To this end, the following particular subjects are studied.
1. Study of phase vortices in the scattering fields of light
In optical metrology, the phase information is extremely useful since it yields
information with respect to displacement, deformation, and the state of vibration
of objects. To detect the phase of light, a technique of interference of light
is used. That is, the phase information is given by a form of interference
fringes, contour lines of phase. In the fringes observed in the field of light
scattering from rough surfaces, phase vortices appear depending on statistical
properties of scattering objects, and they are quite different from those from
well-polished mirrors with deformation to be small compared with the wavelength
of light used. We are studying the phase vortices for the purpose to reveal
its generating mechanism and to apply to detect the deformation of optical
rough objects.
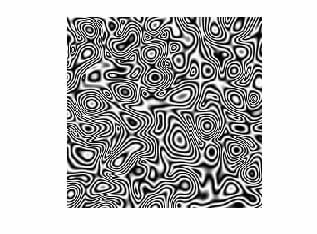

Fringe patterns without (left) and with (right) phase vortices.
2. Digital holography and its application to a security technique of image
information
Both the encoding technique and digital watermarking one of image information
are studied by applying a digital holography which is made in a computer on
a basis of the principle originally developed in the field of optics. Images
randomly phase-modulated are Fourier-transformed and the diffuse-type digital
holograms are constructed by superposing a reference wave onto it. Reconstructed
images from digital holograms are obtained as a pair of images which are corresponding
to real and imaginary images in optical holography. Since the digital holograms
consist of homogeneous intensity distribution under the appropriate condition
of random phase modulation, they can be used as encoding pattern of image information.
In addition, some messages can be embedded in digital holograms as a digital
watermarking. Encoding techniques are useful to protect the digital contents
from malicious attackers in the Internet and digital watermarking techniques
are effective to protect the copyright of owners. Nowadays, these are an emergency
subject with respect to the security of information in communications through
the Internet.
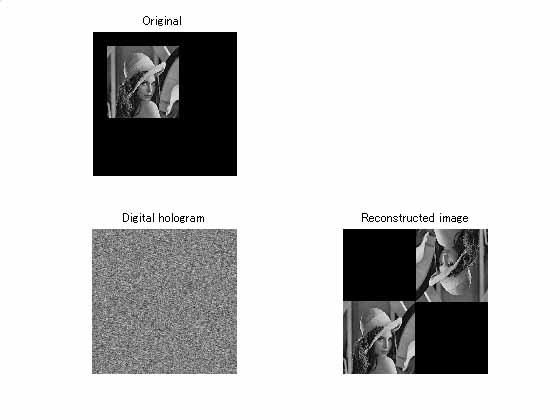

Object image (upper), digital hologram (lower left) and reconstructed images
(lower right)
3. Generation of functional optical waves and advancement of optical metrology
and optical information processing
Recently, attention is attracted to techniques for synthesizing optical waves
and various efforts are made for designing and generating light waves suitable
for particular applications. While most of them are concerned with deterministic
waves, it is also intriguing to extent such an idea to random fields of scattered
light that can be applied to optical metrology and information processing.
For this purpose, in this study, methods are investigated for generating
scattering fields with properties suitable for improving precision and performance
of optical techniques, and the properties of generated optical fields are
analyzed. In particular, properties of intensity and phase are investigated
for scattering fields with fractal properties and for those with nondiffracting
properties, which are characterized by long spatial correlations, and their
applications are actually developed
![]()
Optical system for generating nondiffracting fields of scattered light
![]()

Spatial phase distributions of ordinary (left) and fractal (right) fields
of scattered light
4. Development of intelligent measurement and information processing on the
basis of statistical image processing
Information involved in light as spatial and temporal variations of its intensity,
phase, wavelength or other parameters is detected as image data. Images obtained
in this way may contain random features in some way, whether they are a natural
image, interference fringe pattern, scattering pattern or spectroscopic image,
and hence statistical approaches play an important role in their processing.
In this study, therefore, by devising and applying mathematical and statistical
processings suitable for specific purposes, methods are developed for extracting
latent information from the image. In doing so, various advanced techniques
such as wavelet, fractal, bispectral and multivariate analyses are exploited
to perform effective extraction and intelligent processing of information and
to develop high-precision measurement and processing.
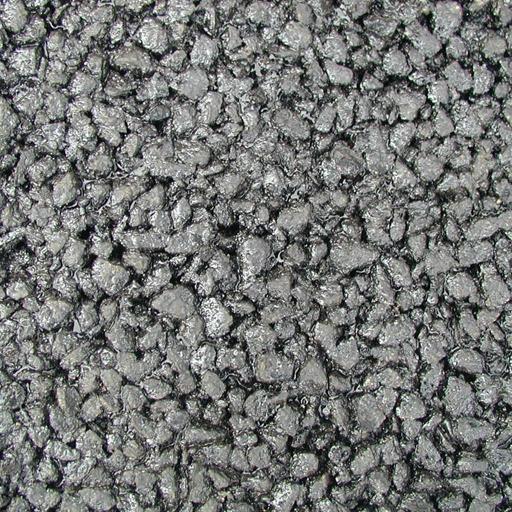

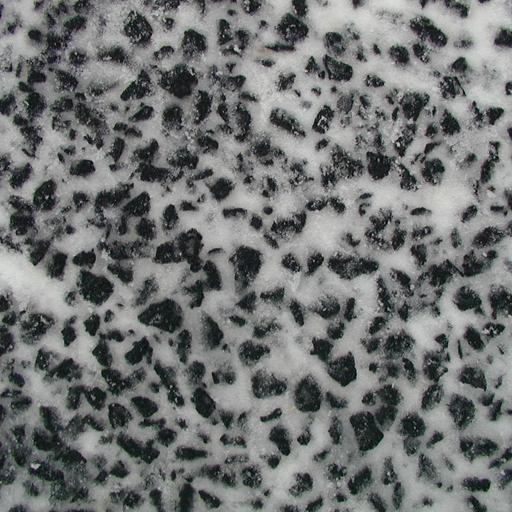
Images of porous asphalt concrete in dry (left) and snow/ice (right) conditions
5. Development of intelligent measurement and information processing
on the basis of wavelength domain information
By focusing on information contained in wavelength domain, among various parameters
characterizing optical waves, techniques are developed in this study for measurement
and information processing on the basis of spectral information of detected
waves. In particular, by devising data processing for effectively retrieving
desired information from spectra of such objects as biomedical tissues and
foods with complex components and internal structures, optical measurement
techniques based on spectral analyses are developed. Attention is also paid
to the phenomenon of structural color, and relations of structures and spectra
are elucidated. Further studies are also made to develop methods for discriminating
and recognizing images of various objects on the basis of spectral information.

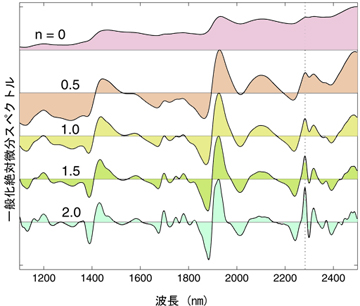
Near infrared absorption spectra of rice (right) and their generalized absolute
derivatives (right)
>> Speech and language information processing group
>> Robot and control information processing group