>> Top >> Project >> Main research results >> Vision and image information processing group
![]()
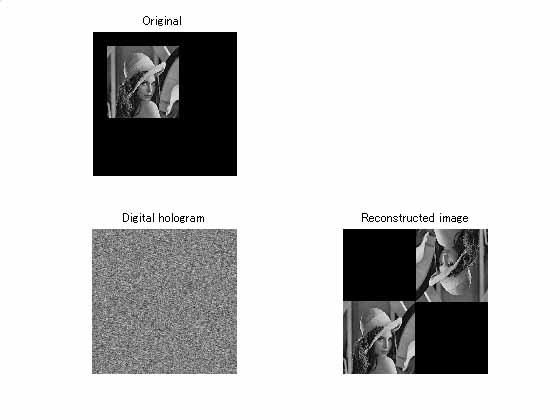

Object image (upper), digital hologram (lower left) and reconstructed
images (lower right)
Generation
of fractal fields of scattered light and their properties.
By devising optical systems for producing light scattering
phenomena, it is possible to generate scattered light fields with fractal
properties such
as self-similarity and power-law correlation. So far, such methods have been
proposed theoretically and demonstrated experimentally. In the present study,
further considerations were given on the basis of computer simulations and
some new knowledge was obtained concerning the conditions of the illumination
optics for the scattered fields to have fractality and concerning multifractality
of the scattered fields.
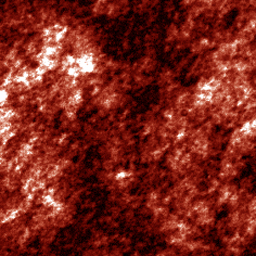
Intensity distribution of a fractal field of scattered
light (experiment)
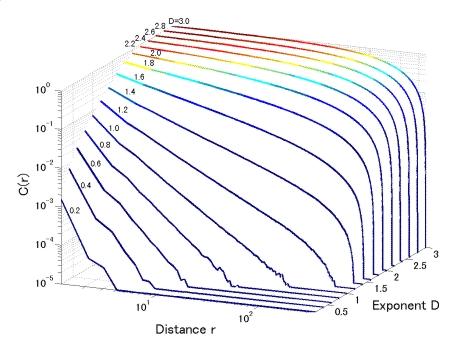
Correlation functions of the intensity fluctuations of fractal fields of scattered light(computer simulation)
Generation of nondiffracting
fields of scattered light and their applications
A light beam that keeps its shape and size during free-space propagation
is called nondiffracting and a Bessel beam is known as one of most typical
nondiffracting beams. It was shown that it is possible to provide scattered
fields with such a property, and generated nondiffracting scattered fields
were applied to develop a method for measuring in-plane motion of an object
with high out-of-plane insensitivity. The figure on the right shows measurement
curves for two cases of in-plane motion only and of combined motions of in-
and out-of-plane with the latter 100 times larger than the former. Two curves
are almost identical, indicating high insensitivity to the out-of-plane motion
of the object.
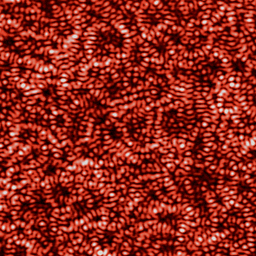
Intensity distributions of a nondiffracting
field of scattered light (experimental)
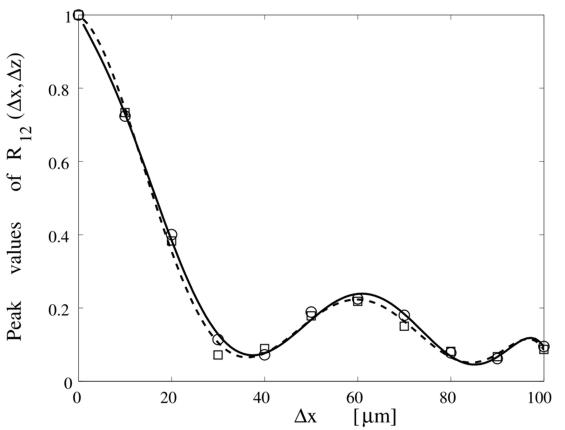
Measurement of motion of an object using nondiffracting
scattered fields. Results in the cases of in-plane motion only (broken
line) and of combined motions of in- and out-of-plane with the latter 100
times larger than the former(solid line)
Discriminant methods of winter pavement conditions
Winter pavement shows various appearances depending upon its kind and
snow conditions. To develop methods for automatically discriminating
its conditions from images captured by CCD camera, various statistical
analyses are applied to different pavement images. One of the results
is shown in the following figure. Six different conditions for two kinds
of pavement are roughly discriminated by means of three parameters of
skewness and contrast derived from probability density functions and
fractal dimension of the pavement images.
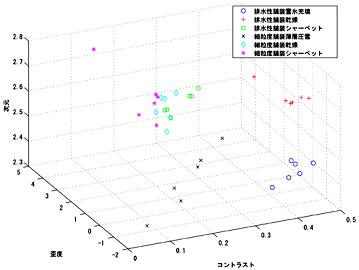
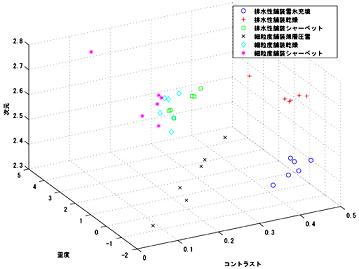
Discrimination of winter pavement conditions by means of fractal dimension
of the images
(the left and right figures constitute a stereogram).
Near infrared spectral analysis by means of generalized differentiations
Spectra in the near infrared region have properties suitable for analyzing constituents
of complex organic objects such as biomedical tissues, agricultural products
and foods, and hence analyses on the basis of the near infrared spectroscopy
(NIRS) are expanding rapidly into various industries. In this study, to further
improve the performance of NIRS, data processing based on generalized differentiations
is applied. The following figure shows a result of correlation map between
generalized derivative spectra of rice flour and its major constituents (amylose,
moisture and protein). As the derivative order increases, correlation peaks
(portions of dark red) narrow in width, separate into two or more, and/or emerge.
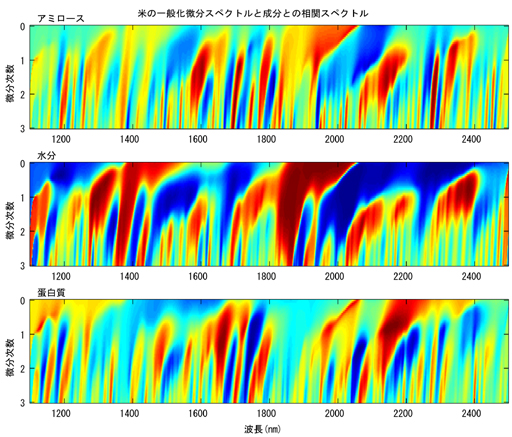
Correlation spectra between generalized derivative spectra
of rice flour and its major constituents (amylose, moisture and protein)
>> Speech and language information processing group
>> Robot and control information processing
group